At Earth Dental Hospital, we believe in the importance of maintaining healthy teeth and gums for a lifetime of smiles. While most people are familiar with cavities and tooth decay, one of the most serious, yet often overlooked, dental conditions is periodontal disease, or gum disease.
Periodontal disease affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to severe complications if left untreated. In this blog, we’ll explain what periodontal disease is, its symptoms, and how it can be prevented and treated.
What is Periodontal Disease?
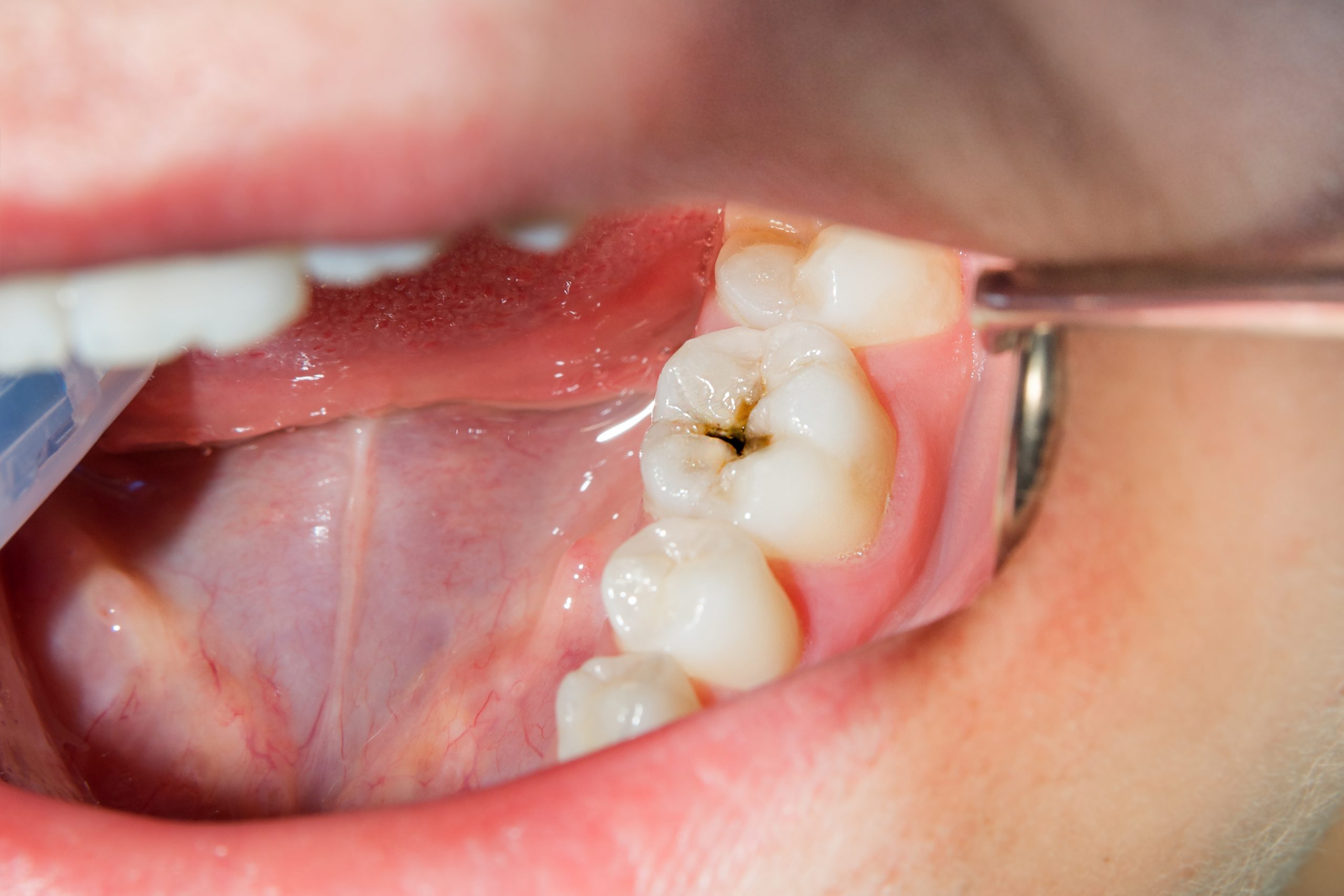
Periodontal disease refers to an infection of the tissues that surround and support your teeth. It begins with the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional.
As the plaque and tartar build up, they cause irritation and inflammation of the gums, which can progress to more serious forms of gum disease if not addressed. There are two main stages of periodontal disease:
-
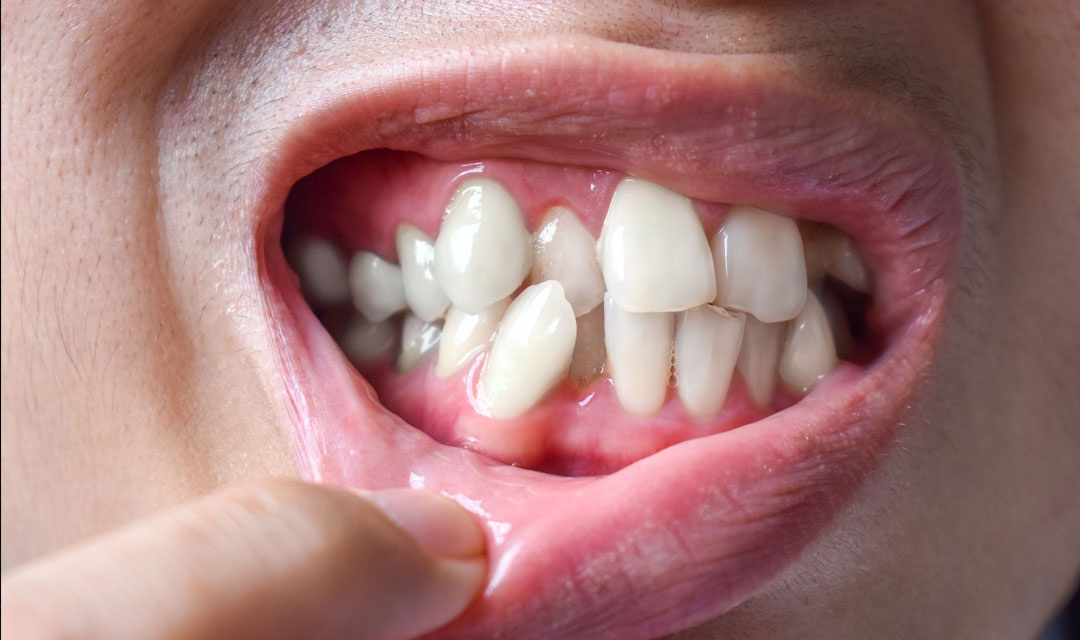
Gingivitis: The earliest stage of gum disease, gingivitis, is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. It is usually painless, which is why many people don’t realize they have it. Fortunately, gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional cleaning.
-
Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe stage. At this point, the infection spreads to the deeper tissues and bone supporting the teeth. It can lead to tooth mobility and even tooth loss if not treated.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease often progresses silently, with few noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, there are signs to watch out for:
-
Gum bleeding: Gums that bleed while brushing or flossing are one of the first signs of gum disease.
-
Swollen or red gums: Healthy gums should be firm and pale pink. If your gums are swollen, red, or tender, it could be a sign of infection.
-
Bad breath (halitosis): Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth could be a result of the bacterial buildup associated with gum disease.
-
Receding gums: If your gums are pulling away from your teeth, making them appear longer, this is a sign of gum disease.
-
Tooth mobility: In advanced stages, teeth may loosen or shift positions, which is a clear sign of severe gum disease.
How Periodontal Disease Affects Your Overall Health
While gum disease primarily affects your oral health, research has shown that it can also have far-reaching effects on your overall health. Studies suggest a link between periodontal disease and conditions such as:
-
Heart Disease: Chronic inflammation caused by gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, including heart attacks and strokes.
-
Diabetes: People with diabetes are more susceptible to gum disease, and gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels.
-
Respiratory Issues: Bacteria from infected gums can be inhaled into the lungs, leading to respiratory infections, especially in people with chronic lung diseases.
-
Pregnancy Complications: Gum disease may increase the risk of premature birth or low birth weight, which is a concern for pregnant women.
Preventing Periodontal Disease
The good news is that periodontal disease is preventable with the right care and habits. Here are some steps you can take to reduce your risk:
-
Brush your teeth twice a day: Make sure to brush for at least two minutes with fluoride toothpaste. Don’t forget to brush your tongue as well, as it can harbor bacteria.
-
Floss daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and below the gumline, areas that a toothbrush can’t reach.
-
Use an antimicrobial mouthwash: A mouthwash can help reduce plaque and bacteria in your mouth, preventing the development of gum disease.
-
Regular dental check-ups: Regular visits to your dentist are crucial for early detection of gum disease. A professional cleaning can remove tartar and plaque buildup, which is key in preventing periodontal disease.
-
Stop smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease and can impair healing after treatment.
Treatment for Periodontal Disease
If you are diagnosed with periodontal disease, the treatment will depend on the severity of the condition. Early-stage gingivitis can typically be treated with improved oral hygiene and professional cleaning. However, more advanced periodontitis may require more intensive treatments, including:
-
Scaling and root planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the surfaces of the tooth roots to prevent further buildup.
-
Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control bacterial infection in the gums.
-
Surgical procedures: For severe cases, surgical options such as flap surgery or bone grafts may be necessary to restore the gum and bone health.
Conclusion
At Earth Dental Hospital, we are committed to helping you achieve and maintain optimal oral health. If you notice any signs of gum disease or if it’s been a while since your last dental check-up, don’t wait to get the care you need.
Periodontal disease is preventable, and with early detection and proper treatment, you can protect your smile and overall health. If you’re concerned about your gums or have questions, feel free to contact us for more information or schedule an appointment with one of our experienced dental professionals.
Call us today at Earth Dental Hospital, and take the first step toward a healthier smile and better overall well-being!